Bank of Canada Statistics: Canadian homeowners are facing a crossroads. As of April 2024, the Bank of Canada’s key interest rate is 5%. This significant increase has thrown a wrench into mortgage plans, leaving many wondering. The Canadian real estate market has been experiencing a notable trend for the past few years. Homeowners and potential buyers are confronted with a dilemma as a result of the recent interest rate hike: should they choose a short-term mortgage or lock in their mortgage rates now? This comprehensive guide will analyze the benefits and drawbacks of each option, providing valuable insights to help you make an informed decision.
Before discussing the details of short-term mortgages and rate locking in variables, it is important to investigate the two main categories of mortgages: fixed-rate and variable-rate.
| Fixed-rate Mortgages | Variable-rate Mortgages |
| A fixed-rate mortgage entails a perpetually fixed interest rate for the duration of the loan. This category of loan offers stability due to the fixed monthly payments, which remain constant regardless of fluctuations in the market interest rates. | An adjustable-rate mortgage, or variable-rate mortgage, carries a variable interest rate that is subject to change over a while. The adjustments are calculated relative to a benchmark interest rate, such as the prime rate. |
Each type has its characteristics and considerations, which are important to understand before making a decision.
| Feature | Fixed-Rate Mortgage (30 years) | Variable-Rate Mortgage (5 years initial fixed, then adjustable) |
| Initial Interest Rate | 5.50% | 4.80% |
| Monthly Payment (Year 1) | $2,200 | $1,900 |
| Interest Rate Changes | None | May adjust after year 5, and every year thereafter |
| Potential Payment Changes in a Rising Rate Environment | None | May increase significantly if interest rates rise |
| Stability | Offers stability with predictable monthly payments. | May start lower but can change, leading to payment variations. |
| Market Dependency | Independent of market fluctuations, providing security. | Dependent on market rates, exposing borrowers to risk. |
| Budgeting | Facilitates accurate budgeting with constant payments. | Requires flexibility in budgeting due to potential rate changes. |
| Risk | Shielded from market volatility, offering peace of mind. | Exposes borrowers to potential rate increases, increasing risk. |
In a hypothetical scenario where market interest rates fluctuate, the differences between fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgages become more evident:
| Year | Market Interest Rate | Fixed-Rate Mortgage Payment | Variable-Rate Mortgage Payment |
| Year 1 | 4% | $1,000 | $900 |
| Year 2 | 5% | $1,000 | $1,050 |
| Year 3 | 6% | $1,000 | $1,200 |
In this example, the fixed-rate mortgage maintains a constant monthly payment of $1,000 throughout the term, providing stability for the borrower. However, the variable-rate mortgage starts with a lower payment of $900 in Year 1 but increases to $1,200 in Year 3 as the market interest rate rises. While the variable-rate mortgage offers initial savings, it also carries the risk of higher payments in the future.
Understanding these differences can help borrowers make informed decisions based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Short-term Mortgages: An Overview
In the context of rising interest rates, Short-term mortgages have gained popularity among Canadian homeowners due to rising interest rates.
As the term typically denotes, a short-term mortgage is a loan with a duration of under five years. This category of mortgage may be variable-rate or fixed-rate. Potentially reduced interest rates are the primary appeal of short-term mortgages in comparison to long-term loans.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ● An important advantage associated with short-term mortgages is the possibility of obtaining lower interest rates. With shorter terms, lenders assume less risk and are, therefore, frequently able to offer more competitive interest rates.
● In addition, short-term mortgages provide greater adaptability. You can more frequently reevaluate your financial situation and adjust the results of a shorter commitment. |
● Nevertheless, short-term mortgages are not without their limitations. One notable drawback is the presence of uncertainty. Upon the expiration of the term, you might be required to pay a greater interest rate if market rates rise substantially, resulting in increased expenses.
● Additionally, frequent renewals could result in increased administrative effort and possible renewal fees. |
Highlighted Market Trend: According to the Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA) stated that national home sales have dipped by 15% compared to last year, indicating a cooling market. This trend aligns with homeowners seeking short-term mortgages, potentially to lock in a lower rate before interest rates climb further, or to strategically time their exit from the mortgage and re-evaluate their options in a potentially more favorable market climate.
Expert Insight and Statistics on Short-Term Mortgage Increase:
Financial experts suggest the rise of short-term mortgages reflects a combination of factors. Homeowners concerned about rising interest rates may be looking to lock in a lower rate for a shorter period. Additionally, some homeowners might be anticipating selling their property within a few years and prefer a shorter mortgage term to align with their plans.
Statistics support this growing preference for short-term mortgages. According to a recent report by the Canadian Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), a government agency focused on housing market analysis, the origination rate of mortgages with terms less than five years increased by 18% in 2023 compared to 2022.
This significant rise indicates a clear shift in homeowner behavior and a strategic response to the changing interest rate environment.
Locking In Mortgage Rates: An Overview
In addition to rate lock and mortgage rate lock, locking in a mortgage rate refers to a lender’s commitment to maintain a particular interest rate for a specified period between loan approval and closing. Generally, the lock-in period lasts between 30 and 60 days; however, an extension is available for an additional charge.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ● There are numerous advantages to locking in your mortgage rate during an environment of rising interest rates. One of the most evident benefits is the assurance it affords. A rate lock assures you that your mortgage rate will remain constant until the scheduled closing date.
● An additional advantage of a rate lock is that it facilitates accurate budgeting. Having prior knowledge of the interest rate enables one to compute monthly payments and verify that they remain within a financial means. |
● Despite their benefits, rate locks may also present certain drawbacks. One notable drawback is the possibility of overlooking opportunities. Even if market rates decline after the lock-in period, you will remain bound by the increased rate.
● Further, the cost of extending a rate lock may increase. To extend the lock, you might be required to pay a significant fee if your home purchase is delayed and the lock period expires. |
In addition to the previously mentioned advantages of locking in your mortgage rate during a period of rising interest rates, securing a fixed rate can also provide significant psychological peace of mind. This emotional security should not be underestimated, as buying a home is often the biggest financial decision an individual makes in their lifetime.
According to the Canadian Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), Locking in a mortgage rate typically involves working with your lender to secure a specific interest rate for a designated period, usually 30 to 60 days. This timeframe allows you to find a home and complete the mortgage approval process without the risk of interest rates rising. There may be a fee associated with locking in your rate, but this cost can be outweighed by the peace of mind and potential savings if rates increase.
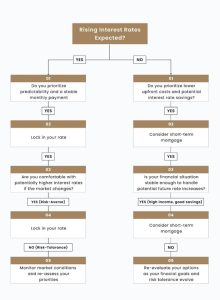
If you prioritize predictability and peace of mind, locking in can be a wise choice, especially in a rising interest rate environment. However, it’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the drawbacks and consider consulting with a mortgage broker or financial advisor registered with the Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA) to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Crucial Factors to Consider Short-Term Mortgage Vs. Locking In
Multiple factors must be taken into account when deciding between a short-term mortgage and rate locking in. A few of them include:
- Market Circumstances: The present and anticipated future market conditions are critical determinants in making this decision. If a substantial increase in interest rates is anticipated, it could be prudent to secure a fixed rate. Conversely, if interest rates remain stable or are anticipated to decline, a short-term mortgage could be more advantageous.
- Financial Conditions and Objectives: Your financial situation and objectives are crucial factors. If you value predictability and stability, a rate lock may be your best bet. On the contrary, if you possess a certain degree of risk tolerance and are eager to capitalize on the possibility of reduced interest rates, a short-term mortgage might be an appropriate selection.
- The Loan Duration: The loan’s term is an essential factor to contemplate. Rate locking can provide long-term stability for those in the market for a long-term mortgage. However, if you are contemplating a loan with a shorter term, a short-term mortgage may provide lower interest rates.
- Financial Advisors: For personalized advice on your specific situation, consider consulting a mortgage broker or financial advisor registered with the Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA).
Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance: Detailed breakdown of how individual financial goals and market conditions influence this decision.
Young Couple Planning to Expand Their Family: Let’s say Sarah and David (early 30s, dual income) are planning to buy their first home and may consider starting a family within 5-7 years. They prioritize stability and are risk-averse.
- Market Conditions: If interest rates are stable or predicted to rise, locking in could be beneficial. This ensures a predictable monthly payment throughout the short term, allowing them to save for future expenses like childcare.
- Risk Tolerance: Sarah and David prioritize stability, so locking in might be wise, even if rates dip slightly. They can re-evaluate their mortgage strategy when their family expands and their financial picture changes.
Retiree with a Fixed Income: John (65, retired) is looking to downsize and needs a mortgage with a manageable monthly payment.
- Market Conditions: If interest rates are high and expected to remain steady or decline, a short-term mortgage could be suitable. John can potentially secure a lower interest rate compared to a long-term fixed rate.
- Risk Tolerance: John has a limited risk tolerance due to his fixed income. He might be comfortable with some fluctuation in rates if it translates to significant initial savings. However, a sudden and substantial interest rate increase could strain his budget.
The Bottom Line
The decision regarding whether or not to lock in your mortgage rate or secure a short-term mortgage is primarily determined by your circumstances as well as the current conditions of the market. It is advisable to seek the advice of a mortgage professional or a financial advisor to arrive at a well-informed decision. This is in addition to analyzing the benefits and drawbacks of each alternative under consideration.
Before you put your signature on the mortgage agreement, you must completely understand every aspect of the mortgage, regardless of whether you choose a home loan with a fixed interest rate or a short-term mortgage. Maintain an active stance, make sure you ask all the questions you need to and make sure that the terms of your mortgage are satisfactory to you. Regarding the ever-changing housing market in Canada, maintaining knowledge and exercising discernment can significantly increase the likelihood of obtaining a mortgage that is in line with one’s financial goals and satisfies the requirements.


