The Bank of Canada recently made a significant move by cutting its policy interest rate by 50 basis points, lowering it to 3.75%. This decision marks the fourth consecutive rate cut and signals the bank’s commitment to supporting economic growth and keeping inflation in check. This move comes as inflation shows signs of cooling down and economic headwinds continue to impact Canadian consumers and businesses. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the reasons behind this decision, its potential impacts on various sectors, and what Canadians can expect in the coming months.
What Is the Bank of Canada’s Policy Rate and Why Does It Matter?
The Bank of Canada’s policy interest rate often called the overnight rate, is a powerful tool used to influence the Canadian economy. It directly affects the interest rates banks charge on loans, including mortgages, lines of credit, and business loans. Here’s why it matters:
- Policy Rate Explained: The overnight rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow and lend money to each other overnight. When the Bank of Canada lowers this rate, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money, which they can then pass on to consumers and businesses in the form of lower interest rates on loans. This encourages borrowing and spending, stimulating economic activity. Conversely, raising the overnight rate makes borrowing more expensive, which can help to cool down an overheated economy and curb inflation.
- Implications of Rate Adjustments: Rate cuts and hikes have a ripple effect throughout the economy. Lower rates tend to stimulate consumer spending and business investment, leading to increased demand for goods and services, job creation, and overall economic growth. However, they can also contribute to inflation if demand outpaces supply. Higher rates, on the other hand, can help to control inflation but may also slow down economic growth.
Understanding the Recent Rate Cut Decision On October 23, 2024, the Bank of Canada announced a 50 basis point reduction in its policy interest rate, bringing it down to 3.75%. This substantial cut aims to:
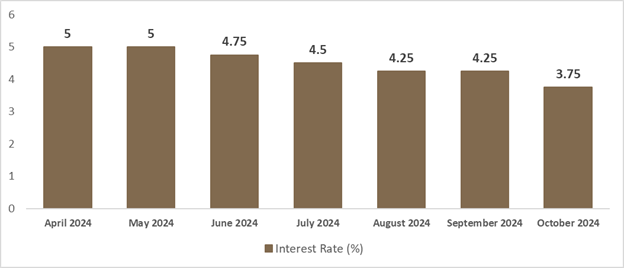
- Maintain Inflation Around the 2% Target: Inflation has been on a downward trend, falling from 2.7% in June to 1.6% in September. This rate cut is intended to support economic growth while ensuring that inflation remains within the Bank of Canada’s target range of 1% to 3%.
- Provide Economic Relief: The Canadian economy is facing challenges such as slow growth and excess labour supply. The rate cut is designed to provide some relief by encouraging borrowing, spending, and investment.
- Prioritize Economic Growth: With inflation stabilizing, the Bank of Canada has shifted its focus to supporting economic growth. This rate cut signals their confidence in the economy’s ability to handle lower interest rates without triggering excessive inflation.
Key Economic Indicators Influencing the Bank of Canada’s Decision
Several key economic indicators played a crucial role in the Bank of Canada’s decision to cut the policy interest rate:
- Inflation Trends: The significant decline in inflation and its projected path towards the target range was a major factor. This suggests that the economy is not overheating and can handle lower interest rates.
- Employment and Wage Growth: The Bank of Canada also considered labour market conditions, including the unemployment rate, wage growth, and productivity. While the unemployment rate remains elevated, wage growth has been moderate, indicating that there is still slack in the labour market.
- GDP Growth: Current and projected GDP growth rates also influenced the decision. While GDP growth has been slow, the Bank of Canada expects it to pick up gradually, supported by lower interest rates.
Impacts on Canadian Economy: Inflation, Employment, and GDP
Lower interest rates are expected to have a positive impact on the Canadian economy through various channels:
- Consumer Spending: Reduced borrowing costs make it more affordable for consumers to finance purchases, such as cars and homes, and to take on debt for other purposes. This can lead to increased consumer spending, which is a major driver of economic growth.
- Labour Market: Lower interest rates can stimulate business investment, leading to job creation and lower unemployment. This can be particularly beneficial for youth and newcomers who often face higher unemployment rates.
- Impact on the Canadian Dollar: A rate cut can put downward pressure on the Canadian dollar (CAD). This makes Canadian exports cheaper for other countries to buy, potentially boosting industries like lumber, energy, and manufacturing. However, it also makes imports more expensive for Canadians, potentially contributing to inflation. You could mention how this might affect the cost of imported goods like electronics or travel.
- Tourism: A weaker CAD could attract more international tourists.
- Technology: Lower rates could encourage investment in Canadian tech startups.
- Agriculture: A weaker CAD can make Canadian agricultural exports more competitive.
- GDP Growth Outlook: The Bank of Canada projects that GDP growth will improve from 1.2% in 2024 to 2.3% by 2026, supported by lower interest rates and other factors. This suggests that the rate cut will contribute to a gradual but steady economic recovery.
The Effect of Rate Cuts on Housing, Mortgages, and Real Estate
The housing market is highly sensitive to interest rate changes. Lower rates can have a significant impact on affordability and demand:
- Mortgage Rates and Home Buying: Lower interest rates translate to lower mortgage rates, making it more affordable for people to buy homes. This can lead to increased demand for housing and potentially higher home prices. Lower rates can also make it attractive for existing homeowners to refinance their mortgages at lower rates, freeing up cash flow for other expenses.
- Real Estate Demand: The rate cut could lead to a rebound in the housing market, with increased demand for both new and existing homes. This could boost residential investment and contribute to economic growth.
- Regional Housing Market Impacts:
- Toronto & Vancouver: These markets are already hot, and lower rates could further increase demand and prices, exacerbating affordability concerns.
- Calgary & Edmonton: These markets are more tied to the energy sector, so lower rates might provide a modest boost, but their recovery is also dependent on oil prices.
- Atlantic Canada: Lower rates could attract more people to relocate to more affordable areas, potentially stimulating local economies.
- Risks to Affordability: While lower rates can make homeownership more accessible, they can also contribute to rapid price increases, especially in markets with limited housing supply. This could raise concerns about affordability and potentially lead to a housing bubble.
Projected Economic Growth for Canada: Short-Term vs. Long-Term Forecast
The Bank of Canada anticipates a gradual strengthening of the Canadian economy over the next few years, fueled by lower interest rates, increased consumer spending, business investment, and exports.
- Short-Term Projections (2024-2025): The economy is expected to continue its recovery from the recent slowdown, with GDP growth gradually picking up. Lower interest rates will play a supportive role by encouraging spending and investment.
- Long-Term Forecast (2025-2026): The Bank of Canada projects continued growth, with positive impacts on various sectors, including technology, renewable energy, and manufacturing. These sectors are expected to benefit from increased investment and innovation, contributing to long-term economic prosperity.
Risks and Considerations: Global Markets, Labor, and Consumer Behavior
While the outlook for the Canadian economy is generally positive, several risks and uncertainties could influence its trajectory:
- Oil Prices and Global Conditions: Canada is a major oil producer, and fluctuations in global oil prices can significantly impact its economy. Lower oil prices could dampen economic growth, while higher prices could contribute to inflation. Global economic conditions, such as slowdowns in major economies like the US or China, could also negatively affect Canada’s growth prospects.
- Global Economic Slowdown: A significant slowdown in the US or China would impact Canada’s exports and overall economic growth.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Events like trade wars, political instability, or conflicts can create uncertainty and negatively affect investment and economic activity in Canada.
- Climate Change: Increasingly frequent extreme weather events (e.g., wildfires, floods) can disrupt economic activity and infrastructure, requiring costly
- Wage Growth and Labor Market Adjustments: One concern is that wage growth could outpace productivity growth, leading to higher costs for businesses and potentially fuel inflation. The labour market also faces challenges in adapting to technological changes and evolving skill demands, which could lead to structural unemployment.
- Consumer Sentiment and Spending Patterns: Consumer confidence plays a crucial role in economic growth. If consumers are uncertain about the future or worried about their financial situation, they may cut back on spending, which could dampen economic activity. Changes in consumer preferences and spending habits can also impact specific sectors and industries.
What to Expect from the Bank of Canada in Upcoming Months
The Bank of Canada has signalled that further interest rate cuts are possible if the economic situation warrants it. The timing and extent of future cuts will depend on incoming economic data and the Bank’s assessment of the inflation outlook.
- Interest Rate Outlook: While future cuts are likely, they will be data-driven and carefully considered. The Bank of Canada will closely monitor key economic indicators, such as inflation, GDP growth, and labour market conditions, to determine the appropriate course of action.
The next scheduled date for announcing the overnight rate target is December 11, 2024.
- Economic Recovery Prospects: The outlook for the Canadian economy is one of gradual recovery, with steady GDP growth and stable inflation. Lower interest rates will provide support, but challenges remain, and the recovery may be uneven across different sectors and regions.
The Bank of Canada will publish its next full outlook for the economy and inflation, including risks to the projection, in the Monetary Policy Report (MPR) on January 29, 2025.
Advice for Canadians:
- Consumers: Take advantage of lower interest rates to consolidate debt, refinance mortgages, and make major purchases if your financial situation allows. However, be mindful of taking on too much debt and avoid overextending yourself financially.
- Investors: Consider investment opportunities that may benefit from lower interest rates, such as those in the housing market or sectors with strong growth potential. However, be aware of the risks involved and diversify your investments to mitigate potential losses.
- Businesses: Lower interest rates can provide opportunities for businesses to invest in expansion, research and development, and hiring. However, carefully assess market conditions and make informed decisions based on your specific circumstances.
Stay informed about the evolving economic landscape and the Bank of Canada’s policy decisions. Contact Pegasus Mortgage Lending today to learn more about your options.


