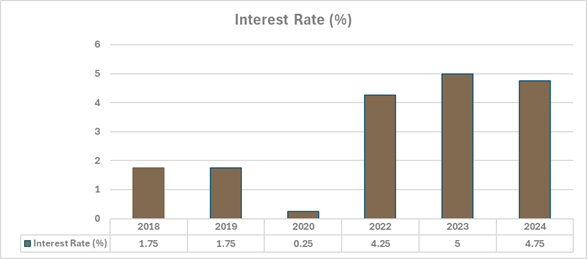
In a significant move that reflects broader global economic trends, Canada’s recent decision to cut interest rates has captured the attention of financial markets worldwide. This strategic move by the Bank of Canada, a reduction of 25 basis points, signals a significant shift in monetary policy and carries potential implications for both the domestic and global economy. By adjusting its interest rates, the Bank of Canada aims to address the complex interplay of inflation, economic growth, and the ever-evolving housing market. This move not only reflects Canada’s specific economic conditions but also holds broader significance as an indicator of global economic trends, influencing factors such as exchange rates, mortgage rates, and overall GDP growth.
At its core, this strategic decision underscores the delicate balance central banks globally strive to maintain between stimulating economic growth and containing inflation, a challenge intensified by the current global economic climate. As you delve deeper into this analysis, you’ll gain expert insights into the backdrop of Canada’s decision, the intricate implications for the economic landscape, and the potential ripple effects on both the domestic and international stage.
Background of Canada’s Decision to Cut Interest Rates
From understanding how changes in the interest rate Canada impact the housing market and mortgage rates to evaluating global reactions and comparisons, this discussion will provide a comprehensive overview. Furthermore, we explore the implications for Canadian citizens, offering a glimpse into how such financial policies influence everyday life, from variable rate mortgages to fixed rate mortgages, and forecast future trends, including interest rate predictions in Canada. This article aims to equip you with a holistic understanding of the significance of Canada’s interest rate cut, setting the stage for informed dialogue and reflection on its far-reaching impacts.
Historical Context:
Canada’s decision to reduce interest rates is rooted in a historical context characterized by fluctuating economic indicators and pressures from both domestic and global economic environments. Historically, the Bank of Canada has adjusted rates to manage economic stability, targeting inflation and unemployment levels. This strategic move is seen as a response to the need for maintaining economic growth while managing inflationary pressures that have been evident in various sectors of the economy.
Key Reasons Behind the Decision:
- The primary reasons behind Canada’s decision to cut interest rates include the desire to stimulate economic growth and to alleviate the financial burdens on households and businesses. By lowering the interest rates, the Bank of Canada aims to encourage borrowing and investing, which in turn can lead to increased consumer spending and business expansion.
- Additionally, this decision is intended to counteract the economic slowdown triggered by global uncertainties and to ensure that inflation rates remain within the target range set by the central bank. This approach reflects a proactive measure to bolster the economy against potential downturns and to support the financial well-being of Canadian citizens.
Economic Effects of the Interest Rate Cut
| Impact on Inflation | Effect on GDP Growth |
| The recent decision by Canada to cut interest rates is expected to significantly affect inflation. Initially, the cut is aimed at boosting consumer spending, which could, in turn, lead to higher inflation rates. However, the overall impact on inflation will vary depending on several factors including the strength of the labor market, consumer confidence, and the general state of the economy. This multifaceted approach indicates that while the intent is to stimulate economic activity, careful monitoring is required to manage potential inflationary pressures effectively. | Furthermore, the interest rate reduction is anticipated to have a positive impact on GDP growth. By making borrowing more affordable, the rate cut encourages businesses to invest and consumers to spend more, potentially leading to an uptick in economic activity. Economists suggest that this could substantially boost Canada’s economic growth, although the extent of this impact will largely depend on the market and consumer responses to the new monetary policy. This strategic financial maneuver is designed to navigate through current economic uncertainties and stimulate growth, reflecting a proactive stance by the Bank of Canada in managing the country’s economic trajectory. |
Global Reactions and Comparisons
Analysis: Canada’s Unique Position in Interest Rate Policy
Canada’s proactive stance in reducing interest rates stands out amongst its G7 peers. It was the first nation to initiate rate cuts in the current economic cycle, a decision attributed to its robust fiscal health, marked by relatively low deficits and a commitment to further deficit reduction. This contrasts sharply with the cautious approach of other G7 nations like the U.S. and those in the European Union, who are still grappling with the economic fallout of the pandemic.
| Factor | Canada’s Situation | Implications for Interest Rate Policy |
| Fiscal Health | Relatively Strong | More flexibility to adjust rates |
| Economic Recovery | Steady | Confidence in absorbing rate cuts |
| Inflation | Manageable | Less pressure to maintain high rates |
Canada’s Groundbreaking Interest Rate Reduction serves as a Catalyst for Global Monetary Policy Shifts:
- Early Mover: Canada’s early move to cut rates underscores its confidence in the Canadian economy’s ability to withstand potential inflationary pressures.
- Fiscal Strength: Canada’s relatively strong fiscal position provides the Bank of Canada with more flexibility in its monetary policy compared to its counterparts burdened with higher debt levels.
- Global Attention: This move has caught the attention of global financial leaders, influencing discussions on international monetary policy and potentially leading to similar actions in other nations.
Global financial leaders have acknowledged Canada’s decision, noting its significance in the broader context of international monetary policy. Statements from various central bank officials across the G7 have highlighted the importance of cautious yet responsive monetary policy adjustments in light of global economic uncertainties. The European Central Bank, for instance, has indicated a readiness to follow suit, albeit more cautiously, emphasizing the balancing act central banks must perform to support economic recovery while managing inflation. These reactions underline the interconnectedness of global economies and the ripple effects of monetary policies implemented by G7 nations.
Implications for Canadian Citizens
1. Impact on Mortgage Rates
The recent interest rate cut by the Bank of Canada has immediate implications for homeowners, particularly those with variable-rate mortgages. For instance, a homeowner with a variable-rate mortgage on a home valued at approximately $700,000 saw their monthly payments decrease from $4,157 to $4,061, saving nearly $100 each month or about $1,152 annually. This reduction in interest rates directly benefits those with variable-rate mortgages by decreasing their monthly financial burden, allowing them to allocate funds to other essential expenses.
2. Changes in Consumer Spending
The adjustment in interest rates also influences consumer spending patterns. For example, Joseph Hopkinson, a variable-rate mortgage holder, noted that the rate cut would save his family an equivalent of a week’s groceries, approximately $142 per month. This shift in disposable income can lead to increased consumer spending, particularly among higher-income demographics who are more likely to increase their spending sooner compared to those with lower incomes. This trend suggests that businesses catering to higher-income consumers may experience better financial performance in the near future.
Future Outlook and Predictions
Looking forward, the significance of Canada’s monetary policy adjustment extends beyond its immediate economic ramifications, suggesting a landscape ripe with both opportunities and challenges. As the international community watches and, in some cases, begins to mirror Canada’s pioneering stance, the potential for further collaborative or competitive monetary adjustments looms large. This dialogue further emphasizes the interconnectedness of global economies and the critical role of informed, strategic policymaking in navigating the complexities of economic growth, inflation, and market stability.
1) Economic Forecasts
- The future outlook for Canadian economy, influenced by the Bank of Canada’s interest rate decisions, hinges on several key economic indicators.
- Analysts closely monitor GDP growth, inflation rates, and consumer spending patterns to forecast economic health and guide strategic decisions.
- With potential rate cuts, the economic landscape is expected to show variability. For instance, if inflation continues to ease and aligns sustainably towards the 2% target, further policy rate reductions could be anticipated.
- However, these decisions will be made cautiously, one meeting at a time, to avoid jeopardizing the progress on inflation.
2) Potential Challenges and Opportunities
- Navigating the future will involve addressing both challenges and opportunities that arise from regulatory changes, technological disruptions, or shifts in consumer preferences.
- For the banking sector, the anticipated rate cuts could ease funding costs and improve bottom lines, offering relief particularly if economic activities bolster as expected.
- However, challenges such as a potential increase in mortgage delinquencies due to payment shocks on renewals loom, necessitating careful monitoring and responsive measures from financial institutions.
By inviting continuous observation and adaptation, Canada’s approach offers a template for economic resilience and innovation, laying the groundwork for ongoing discourse and research into effective monetary policy strategies within the G7 and beyond.
The Bottom Line
Throughout this exploration of Canada’s historic decision to cut interest rates, we’ve navigated the depth and breadth of its implications, underscoring the delicate interplay between monetary policy and economic development. The analysis has revealed the multifaceted impact of this decision, highlighting not only the immediate benefits, such as increased consumer spending and relief for homeowners with variable-rate mortgages, but also the broader economic stimulations anticipated in the form of GDP growth and inflation management. By drawing on expert insights and a comprehensive overview of the economic landscape, this discussion has provided a nuanced understanding of the strategic considerations behind the interest rate cut and its expected ripple effects across both domestic and global stages.


